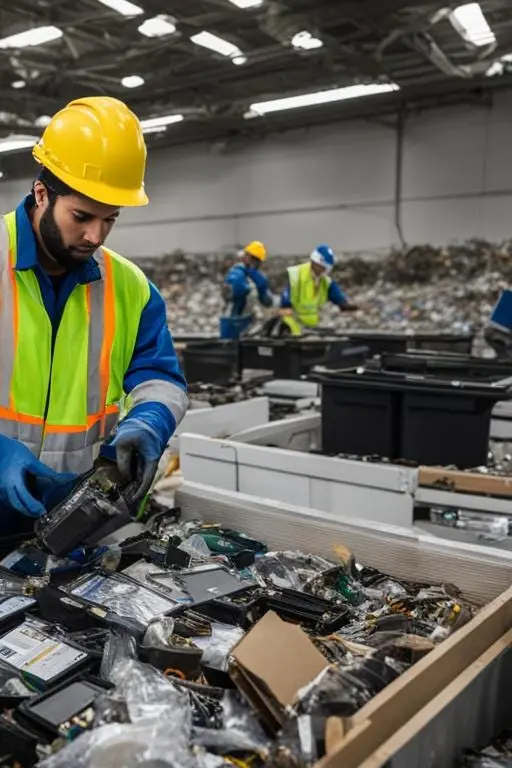
Electronic Waste
Electronic waste (or e-waste) includes all devices that operate using electricity or batteries and are no longer in use. These devices often contain hazardous materials (such as lead, mercury or cadmium), but also valuable secondary raw materials, like copper, aluminum and precious metals.
Proper handling of e-waste is not only important for environmental protection, but also a legal obligation for businesses. Our company offers fully compliant, documented and secure solutions for managing electronic waste.
After July 31, 2023, it is not permitted to trade used complete electrical and electronic equipment freely in Hungary. This type of material can only be transported within the MOHU system. Since Zorka Bróker Kft has not yet joined the MOHU system, you must contact MOHU directly: www.mohu.hu www.mohu.hu

Types of E-Waste We Accept
- IT Equipment: computers, laptops, monitors, printers
- Household Appliances: refrigerators, washing machines, microwaves, boilers, stoves
- Consumer Electronics: televisions, audio systems, DVD players
- Industrial and Commercial Equipment: control cabinets, transformers, disassembled machines
- Components and Accessories: cables, circuit boards, defective parts
Services for Business Partners
We provide comprehensive electronic waste management services tailored for companies:
- Collection and on-site pickup of electronic devices
- Manual loading available upon request
- Disassembly and pre-sorting by material type
- Documented destruction with serial number tracking
- Destruction certificate provided upon request
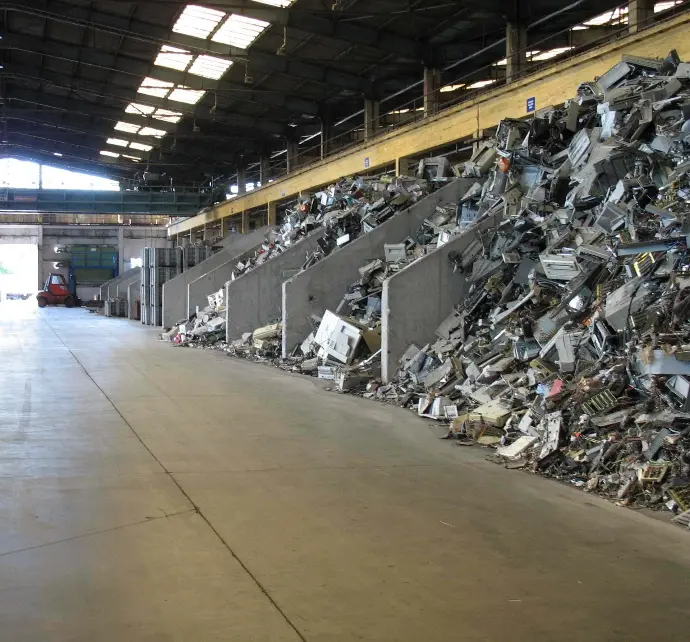


Intake and Pre-Sorting
Devices are recorded and sorted by type (e.g. IT, household, industrial). Hazardous components – such as batteries, refrigerants or display panels – are removed and handled separately.
What Happens to Collected Devices?

Manual Disassembly
Larger devices are manually dismantled to separate key components like motors, wiring, metal frames, and circuit boards. This helps to keep materials clean and suitable for recycling.
Recovery and Disposal
Recyclable materials are transferred to authorized partners for reuse in new production. Non-recyclable and hazardous waste is disposed of in compliance with environmental regulations by certified operators.
Mechanical Processing and Separation
Smaller or complex parts are shredded using industrial-grade equipment. Afterwards, the crushed material is sorted using specialized separation technologies such as magnetic, eddy current and optical sorters to isolate:
- Ferrous and non-ferrous metals
- Plastics
- Electronic components
- Other material fractions